Diet and risk of Barrett's
This thoughtful and thorough analysis of food frequency dietary data from the Melbourne Cohort Study supports previous research indicating that regular intake of leafy vegetables and fruit may independently decrease risk of Barrett's esophagus, in this instance by approximately 40%.
Br J Nutr. 2022 Jul 15;1-28.
doi: 10.1017/S0007114522002112. Online ahead of print.
Diet and risk of Barrett's oesophagus: Melbourne Collaborative Cohort Study
Sabrina E Wang 1 2 , Allison M Hodge 1 2 , S Ghazaleh Dashti 3 4 , Suzanne C Dixon-Suen 2 5 , Natalia Castaño-Rodríguez 6 , Robert Js Thomas 7 , Graham G Giles, Alex Boussioutas, Bradley J Kendall, Dallas R English
PMID: 35837679 DOI: 10.1017/S0007114522002112
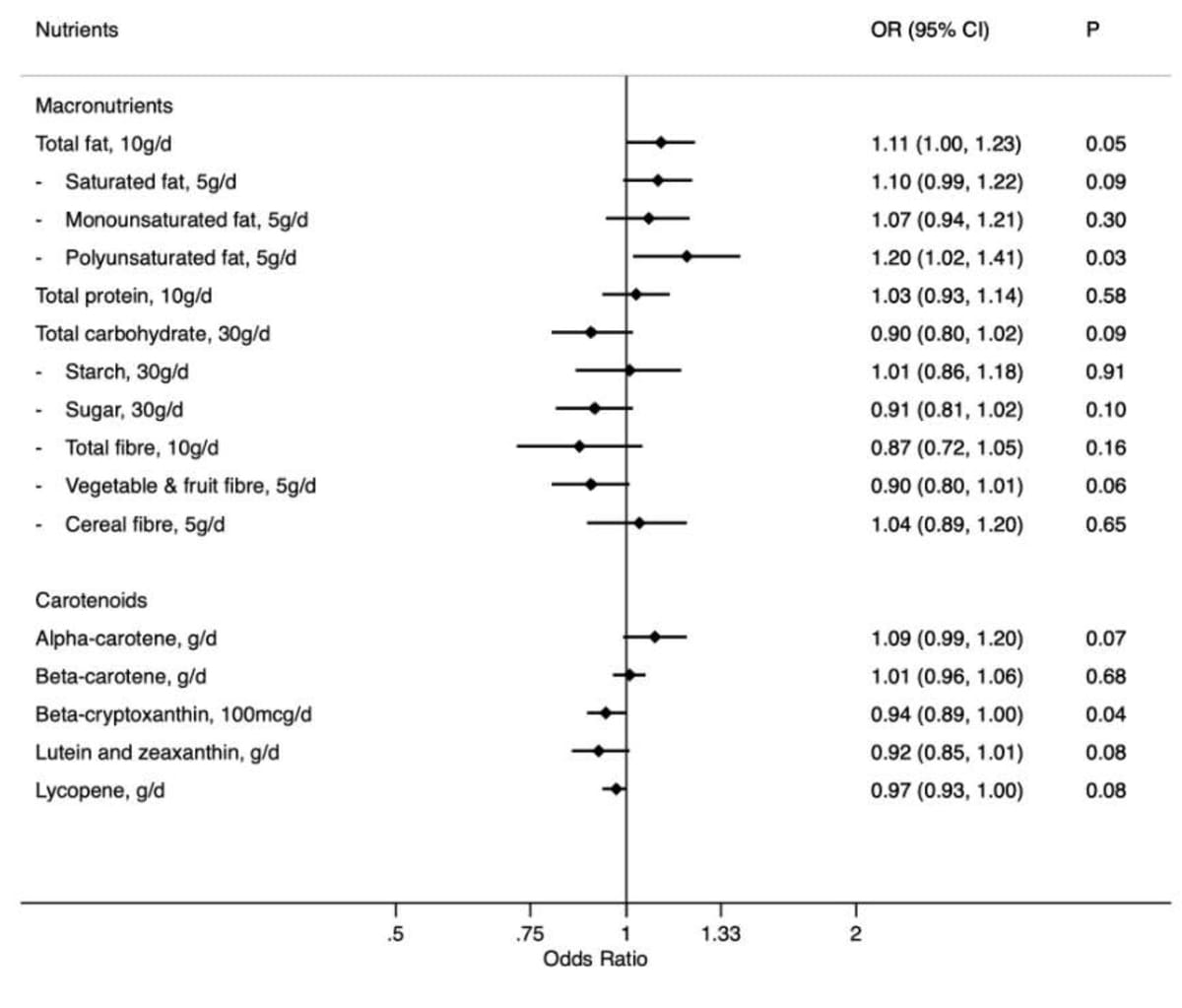
Abstract
Barrett's oesophagus (BE) is the precursor of oesophageal adenocarcinoma, which has become the most common type of oesophageal cancer in many Western populations. Existing evidence on diet and risk of BE predominantly comes from case-control studies, which are subject to recall bias in measurement of diet. We aimed to investigate the potential effect of diet, including macronutrients, carotenoids, food groups, specific food items, beverages, and dietary scores, on risk of BE in over 20,000 participants of the Melbourne Collaborative Cohort Study. Diet at baseline (1990-94) was measured using a food frequency questionnaire. The outcome was BE diagnosed between baseline and follow-up (2007-10). Logistic regression models were used to estimate odds ratios [ORs] and 95% confidence intervals [CIs] for diet in relation to risk of BE. Intakes of leafy vegetables and fruit were inversely associated with risk of BE (highest versus lowest quartile: OR=0.59; CI: 0.38-0.94; p-trend=0.02 and OR=0.58; CI: 0.37-0.93; p-trend=0.02 respectively), as were dietary fibre and carotenoids. Stronger associations were observed for food than the nutrients found in them. Positive associations were observed for discretionary food (OR=1.54; CI: 0.97-2.44; p-trend=0.04) and total fat intake (OR per 10g/d=1.11; CI: 1.00-1.23), the association for fat was less robust in sensitivity analyses. No association was observed for meat, protein, dairy, or diet scores. Diet is a potential modifiable risk factor for BE. Public health and clinical guidelines that incorporate dietary recommendations could contribute to reduction in risk of BE and, thereby, oesophageal adenocarcinoma.